2026 Top Types of Permanent Magnet AC Motors Explained
Permanent magnet AC motors are increasingly popular in various industries. Their efficiency and reliability set them apart from traditional motors. In 2026, understanding the different types of these motors becomes essential. The technology continues to evolve, creating challenges for manufacturers and users alike.
Each type of permanent magnet AC motor has unique features. Some are ideal for low-speed applications, while others excel in high-speed environments. Users must carefully select the right type based on specific needs. Not every choice will suit every application, which can lead to inefficiencies.
As we dive into the different types of permanent magnet AC motors, it's clear that the decision-making process can be complex. Awareness of these intricacies can help avoid potential pitfalls. A deeper understanding will enable better performance and sustainability in various applications.

Overview of Permanent Magnet AC Motors and Their Benefits
Permanent Magnet AC (PMAC) motors are gaining traction in various industries due to their efficiency and performance. These motors utilize permanent magnets to generate a magnetic field. This leads to reduced energy consumption compared to traditional AC motors. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, PMAC motors can improve energy efficiency by up to 25%. This translates to significant savings in operational costs for businesses.
The benefits of PMAC motors extend beyond energy savings. These motors have a compact design, making them suitable for space-constrained applications. Their maintenance requirements are also lower because they have fewer moving parts. A study by the Electric Power Research Institute indicated that maintenance costs can decrease by 15-30% when using PMAC technology. However, there are limitations. The initial cost of these motors can be higher than conventional options. This might deter some companies from adopting this technology.
Despite these challenges, the overall advantages of PMAC motors can outweigh their drawbacks. They are suitable for various applications ranging from industrial machinery to electric vehicles. As technology advances, we may see even more improvements in PMAC motor design and efficiency. Careful consideration is needed when evaluating the switch to PMAC motors. The balance between cost and performance remains a critical factor for many organizations.
Key Types of Permanent Magnet AC Motors: Synchronous vs. Induction
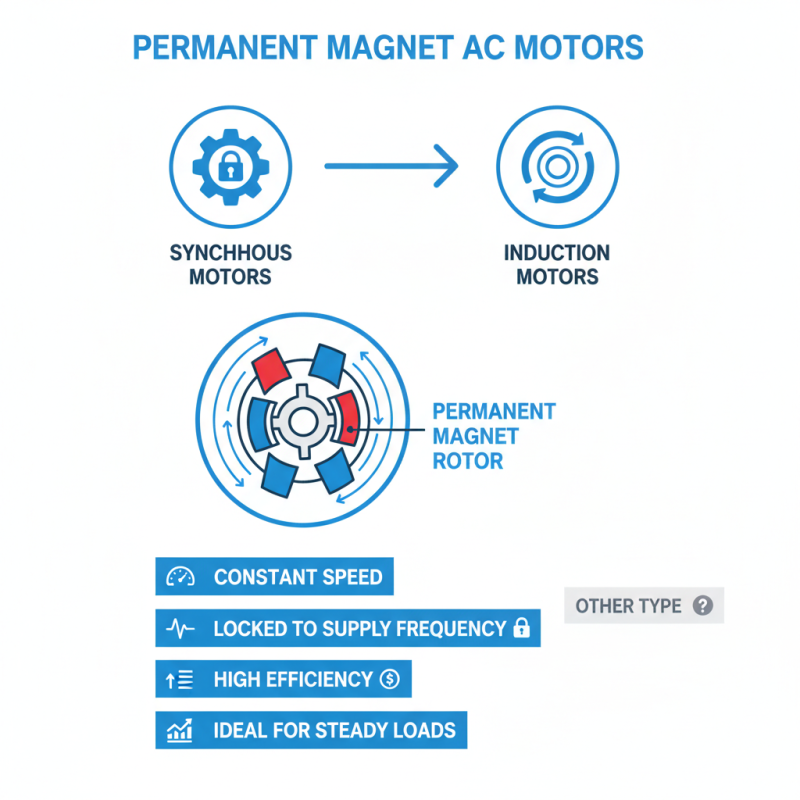
When discussing permanent magnet AC motors, two main types emerge: synchronous and induction motors. Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed, locked to the supply frequency. They require a permanent magnet in the rotor to maintain this alignment. This magnetic force allows for efficient energy use, making them suitable for various applications. They perform well under steady load conditions.
Induction motors, on the other hand, do not use permanent magnets. Instead, they rely on electromagnetic induction to create rotation. This can lead to energy losses. However, they are simpler in design and often more rugged. Many industries favor them for high torque at startup and their lower cost. This versatility allows them to function in diverse environments.
Both types have strengths and weaknesses. Synchronous motors offer precise performance while induction motors excel in robustness. Selecting between them can be challenging. It often requires reflection on specific requirements and limitations of each motor type. In some cases, a hybrid approach could be beneficial, combining the best characteristics of both.
Performance Metrics: Efficiency Ratings and Power Factors
Permanent Magnet AC Motors (PMAC) are rapidly evolving. Their efficiency ratings and power factors are crucial for various applications. A recent industry report highlights that PMAC motors can reach efficiency ratings over 95% under optimal conditions. This efficiency translates into significant energy savings for both industrial and commercial sectors.
Power factors of PMAC motors are another critical performance metric. Often exceeding 0.9, these motors operate effectively while reducing energy loss. In contrast, many traditional AC motors struggle to maintain a power factor above 0.8. This gap indicates a need for better motor selection for efficiency-focused projects. However, optimizing performance often requires careful consideration of load conditions and operating environments.
Some challenges persist. Not all PMAC motors perform consistently across different applications. Factors like temperature and humidity can impact efficiency. Additionally, the initial investment for these motors can be higher compared to their counterparts. Users need to weigh long-term savings against upfront costs. Ultimately, understanding these metrics is essential for making informed decisions in motor selection.
2026 Top Types of Permanent Magnet AC Motors Explained - Performance Metrics: Efficiency Ratings and Power Factors
| Motor Type | Efficiency Rating (%) | Power Factor | Speed (RPM) | Torque (Nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synchronous Motor | 95 | 0.95 | 1500 | 10 |
| Permanent Magnet Brushless Motor | 90 | 0.92 | 3000 | 15 |
| Switched Reluctance Motor | 87 | 0.89 | 2000 | 20 |
| Induction Motor | 88 | 0.87 | 1750 | 25 |
| Stepper Motor | 85 | 0.80 | 1200 | 5 |
Applications of Permanent Magnet AC Motors in Various Industries
Permanent Magnet AC Motors (PMAC) play a vital role in numerous industries today. These motors are known for their high efficiency and compact size. According to a recent industry report, the market for PMAC motors is projected to grow by 10% annually. This growth is fueled by their applications in sectors like automotive, robotics, and energy.
In the automotive industry, PMAC motors are commonly used in electric and hybrid vehicles. They offer better performance and lower energy consumption. A study showed that implementing PMAC motors can improve the efficiency of electric vehicles by 30%. Their lightweight nature also enhances the overall vehicle performance. However, manufacturers still face challenges in scaling production to meet rising demand.
In industrial automation, PMAC motors drive various machinery, enhancing production efficiency. They can decrease operational costs significantly. However, the complexity in controlling these motors can lead to downtime. A report indicated that 15% of companies experience issues related to motor control stability. These challenges need further research to ensure reliable and efficient operation in demanding environments.
2026 Top Types of Permanent Magnet AC Motors
Future Trends and Innovations in Permanent Magnet AC Motor Technology
The field of Permanent Magnet AC (PMAC) motors is evolving rapidly. Recent research indicates a projected growth rate of 10% annually in PMAC motor technology, driven by increasing demand for energy efficiency and reliability. Industries like automotive and HVAC are particularly keen on these advancements. Innovations are focusing on materials and designs that enhance performance while reducing costs.
A key trend is the integration of artificial intelligence in motor controls. This integration aims to improve efficiency and adaptability in real-time operations. Studies show that AI-enhanced PMACs can achieve energy savings up to 30%, a significant improvement from previous generations. However, challenges remain. Adequate data for effective AI training is still sparse. Moreover, the learning curve for engineers to adapt to these technologies can be steep.
Another area of innovation is the miniaturization of components. Smaller PMACs can fit into more compact spaces while maintaining high performance. Innovations like advanced cooling techniques are also emerging, but they come with increased complexity. Cooling solutions can add weight and may not always be feasible in space-constrained designs. The demand for lighter, yet efficient motors poses a dilemma that engineers need to address urgently.
Related Posts
-

Top 7 Benefits of Using Permanent Magnet DC Motors in Modern Applications
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using a Permanent Magnet DC Motor 90V for Your Projects
-

Unlocking the Future: How Imperial Electric Permanent Magnet Motors Enhance Energy Efficiency
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using a 90V Permanent Magnet DC Motor for Your Projects
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Permanent Magnet Motors in Modern Applications
-

10 Tips for Understanding Direct Current Permanent Magnet Motors
