What is a PM Motor and How Does It Work?
A PM motor, or permanent magnet motor, has gained popularity in various applications. Its efficiency and compact design are key benefits that attract many engineers. Unlike traditional motors, PM motors use permanent magnets to generate magnetic fields. This innovation improves performance, making them ideal for applications in robotics, electric vehicles, and appliances.
The unique construction of a PM motor allows for reduced energy loss. Generating torque directly from magnets avoids wasted energy. This is particularly appealing in today's energy-conscious world. However, some challenges remain. The cost of high-quality magnets can be a hindrance. Additionally, temperature variations might affect performance.
Understanding how a PM motor works can lead to better designs and applications. Engineers can optimize their usage by learning about these aspects. An in-depth exploration will reveal both benefits and potential flaws in PM motor technology.
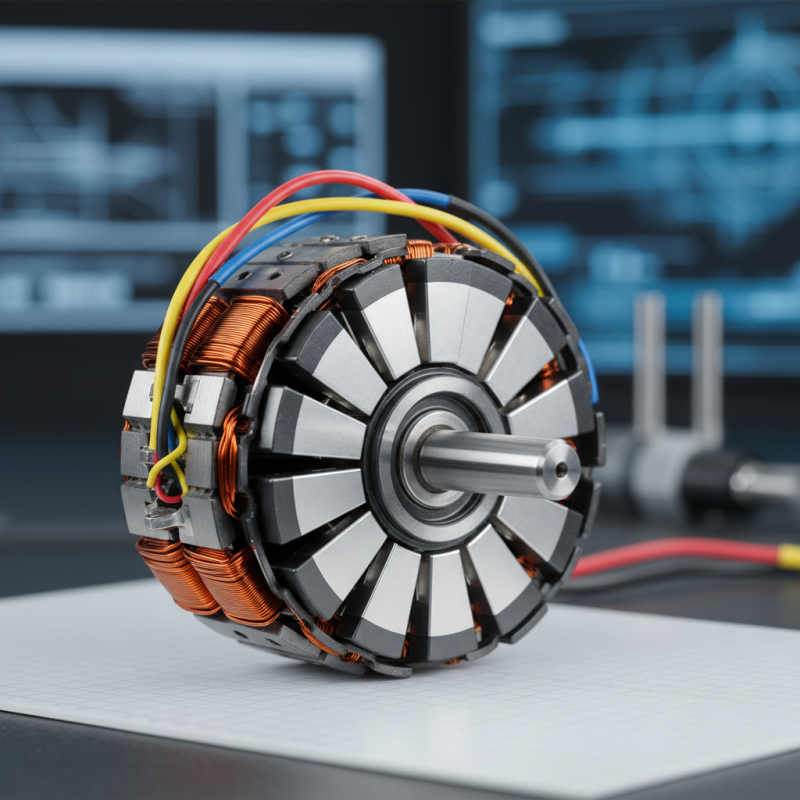
What is a PM Motor?
A PM motor, or permanent magnet motor, operates primarily between two magnetic fields. One field is created by permanent magnets, and the other is generated by electric coils. These two fields interact, generating rotational force. This design provides high efficiency and excellent torque at low speeds.
The simplicity of PM motors is notable. They often require less maintenance than conventional motors. However, they can be sensitive to temperature extremes. Overheating can impact performance and lifespan. Users may overlook this detail during operation. In applications where efficiency is key, the PM motor stands out. Still, it may not perform well under heavy loads. Balancing these factors is essential for optimal performance.
Understanding these nuances helps in choosing the right motor for specific needs. It’s also important to consider the environment where the motor will operate. Factors like humidity and dust can affect efficiency. PM motors are not infallible; careful assessment is necessary.
PM Motor Performance Data
This chart illustrates the performance metrics of a Permanent Magnet (PM) Motor, showcasing its efficiency, torque, power output, and operational speed.
Key Components of Permanent Magnet Motors
Permanent Magnet Motors (PM Motors) are widely used in various applications. They are efficient and reliable, making them a popular choice in industries. Understanding their key components is essential for grasping how they function.
At the heart of a PM Motor lies the rotor. This part contains permanent magnets. These magnets produce a static magnetic field. It interacts with the magnetic field generated by stator windings. The stator is another critical component. It consists of coils wrapped around a core. When electric current flows through these coils, it creates a rotating magnetic field. This interaction between the rotor and stator is crucial for movement.
Another critical aspect is the commutation system. It helps in managing the direction of current in the coils. Without proper commutation, performance drops. There can be inefficiencies, causing overheating. The motor may stall or produce less torque. Understanding these components is vital for maintenance and performance optimization. Each part plays a unique role, influencing the overall efficiency of the PM Motor.
What is a PM Motor and How Does It Work? - Key Components of Permanent Magnet Motors
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Stator | The stationary part of the motor that creates a magnetic field. | Provides the necessary magnetic field for rotor operation. |
| Rotor | The rotating part that interacts with the stator's magnetic field. | Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. |
| Permanent Magnets | Magnets that are fixed in the rotor to create a constant magnetic field. | Eliminates the need for external excitation, enhancing efficiency. |
| Windings | Coils of wire that are energized to create magnetic fields in the stator. | Induces motion in the rotor through electromagnetic interaction. |
| Bearing | Supports the rotor and allows it to spin freely. | Reduces friction and wear for smoother operation. |
How Do PM Motors Generate Motion?

Permanent magnet (PM) motors create motion using magnetic fields. The unique design harnesses the power of magnets to produce torque. Inside the motor, permanent magnets interact with electromagnetic fields from the stator. This interaction generates rotational motion.
The rotor is often equipped with more magnets. This enhances the efficiency of the motor. When the stator is energized, it creates a magnetic field. The rotor then follows this field, generating motion. It's a simple and effective method. However, not all PM motors are energy efficient. Observing their performance in real applications is crucial.
Tips: Ensure proper alignment during installation. Misalignment can lead to inefficiencies. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the motor running optimally. Watch for unusual sounds or vibrations that may indicate problems.
Complex systems sometimes struggle to integrate PM motors effectively. Delays in response time can occur. Always consider the overall design to avoid unforeseen issues. Understanding these nuances helps in optimizing performance.
Advantages of Using PM Motors

Permanent Magnet (PM) motors have gained popularity due to several advantages. Their efficiency is a key factor. According to industry reports, PM motors can achieve efficiencies exceeding 90%. This makes them ideal for applications where energy consumption is crucial. High efficiency translates to lower operating costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
One notable benefit is their compact size. PM motors are smaller than traditional motors with similar output. This feature allows for more design flexibility in various applications. They require less cooling compared to some other types of motors. However, they can be sensitive to temperature extremes, impacting performance. A report from the Electric Power Research Institute notes that while PM motors are highly efficient, operational challenges such as these shouldn't be overlooked.
Another advantage is their capability for precise control. PM motors offer rapid acceleration and deceleration. This is essential in robotics and automation. However, implementing precise control systems can complicate design and integration. The International Electrotechnical Commission highlights this complexity, noting a potential learning curve for engineers. Balancing ease of use with high performance is an ongoing discussion in the industry.
Applications of PM Motors in Various Industries
PM motors, or permanent magnet motors, have gained traction across various industries due to their efficiency and compact design. In manufacturing, they are often used in robotics. Robots equipped with PM motors can perform precise movements. These motors help increase productivity while reducing energy consumption. Tasks that once took hours can now be completed in minutes.
In the automotive sector, PM motors are pivotal for electric vehicles. They provide high torque at low speeds, making acceleration smoother. This is crucial for enhancing the driving experience. Additionally, as more companies shift toward sustainability, PM motors support eco-friendly efforts. They offer an alternative to traditional combustion engines.
Despite their advantages, challenges remain. Cost can be a barrier for some manufacturers. Accessing raw materials for magnets is another concern. Supply chain disruptions can impact production. Companies must weigh these issues against the benefits of efficiency and performance. Continuous improvement is essential for tapping into the full potential of PM motors.
Related Posts
-
How to Choose the Right PM Motor for Your Project?
-

How to Choose the Right PM Motor for Your Application?
-

2025 Top 5 Permanent Magnet DC Motor 180V Options for Enhanced Performance
-

Top 10 Benefits of Neodymium Magnet Motors for Renewable Energy Solutions
-

Top 5 Benefits of Neodymium Magnet Motors You Need to Know
-

Exploring the Future of Energy with Permanent Magnet Motor Generators
