What is Rotor Magnet and How Does it Work in Electric Motors
Electric motors are essential components in numerous applications, ranging from household appliances to industrial machinery, and at the heart of these motors lies the critical rotor magnet. According to Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in electromagnetic engineering, "The efficiency and performance of an electric motor heavily depend on the design and quality of the rotor magnet." With her extensive research into magnetic materials and motor technologies, Dr. Chen emphasizes the pivotal role rotor magnets play in converting electrical energy into mechanical motion.
In understanding how rotor magnets function within electric motors, it is crucial to explore their magnetic properties and how they interact with stator windings. The rotor magnet creates a magnetic field that, when combined with the stator's electric currents, results in torque generation, facilitating the motor's rotation. By delving into the mechanics behind rotor magnets, we gain valuable insights into not only the operational efficiency of electric motors but also the advancements in magnetic technologies that continue to propel the industry forward. Such knowledge is vital for engineers and manufacturers striving to enhance electric motor designs and improve overall energy efficiency.
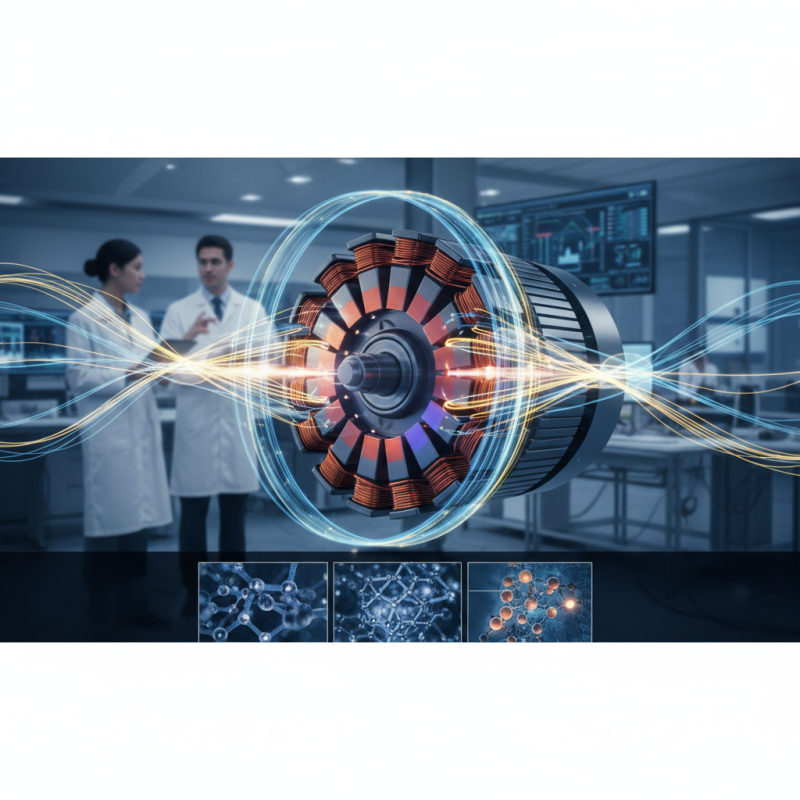

What is a Rotor Magnet in Electric Motors?
In electric motors, a rotor magnet plays a crucial role in the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. Essentially, the rotor is the rotating part of the motor, and it contains permanent magnets or electromagnetic coils that generate a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the stator—the stationary part of the motor—to create motion. The effectiveness of rotor magnets can significantly influence the motor’s efficiency, performance, and overall power output. A recent industry report indicates that motors with high-quality rotor magnets can enhance efficiency levels by up to 20%, demonstrating the importance of this component in modern electric motor design.
When considering the functionality of rotor magnets, it's important to understand the various materials and configurations that can be used. Permanent magnets, typically made from materials like neodymium or ferrite, are favored for their strong magnetic properties. Electromagnets can also be employed, which allow for adjustable magnetic fields and greater control over the motor's operation. These options can vary based on specific applications and performance requirements. According to a market analysis, the preference for advanced rotor magnet materials across various sectors is expected to significantly grow, driven by the demand for more efficient power solutions.
Tips: When selecting electric motors for your applications, prioritize models with high-performance rotor magnets. This can lead to improved energy savings and lower operational costs. Additionally, regularly inspect and maintain your motors to ensure rotor magnets are functioning optimally, as this can prolong the lifespan of your machinery and enhance its reliability.
What is Rotor Magnet and How Does it Work in Electric Motors
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A rotor magnet is a permanent magnet or electromagnet located on the rotor of an electric motor, serving to create magnetic fields that interact with the stator to produce motion. |
| Function | It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy by generating magnetic fields that drive the rotation of the rotor. |
| Types | Permanent magnets or wound coils, based on the type of electric motor. |
| Materials | Common materials include neodymium, ferrite, and aluminum nickel cobalt (Alnico). |
| Applications | Used in various devices such as electric vehicles, household appliances, and industrial machinery. |
| Efficiency | Rotor magnets increase the efficiency of electric motors by reducing energy losses and improving torque production. |
The Role of Rotor Magnets in Motor Functionality
Rotor magnets play a critical role in the functionality of electric motors by providing the necessary magnetic field that drives the motor's operation. In a typical motor setup, the rotor, which is the rotating part of the motor, is equipped with magnets that interact with the stator, creating motion. When electricity flows through the stator coils, it generates a magnetic field that repels or attracts the rotor magnets, resulting in rotation. This interaction between magnetic fields allows the motor to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy efficiently.
Tips: When working with electric motors, ensure that the rotor magnets are correctly aligned. Misalignment can cause inefficient performance or even damage to the motor. Additionally, regular maintenance of the motor's components, including checking for wear and tear on the rotor magnets, is crucial for optimal functionality.
The effectiveness of rotor magnets also depends on their material composition. High-performance magnets, such as neodymium magnets, are often used in modern electric motors due to their strong magnetic properties. These materials enhance the motor's torque and efficiency, making it suitable for various applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Tips: If you're considering upgrading your motor, research various magnet materials and their properties to find the best fit for your specific needs. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of different types of rotor magnets can lead to better performance and longevity of your electric motor.
Types of Rotor Magnets Used in Electric Motors
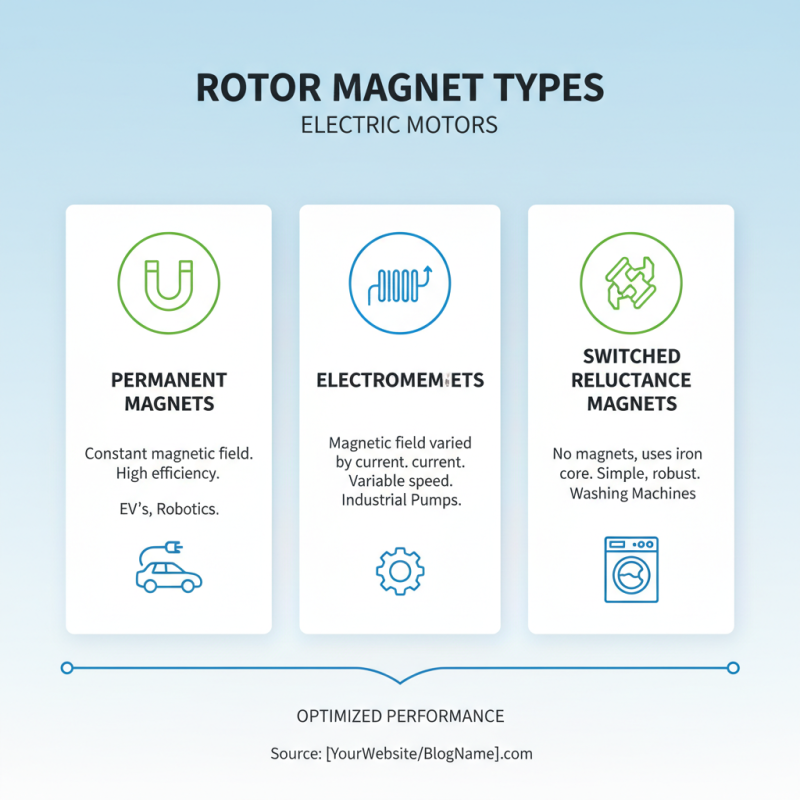
There are several types of rotor magnets used in electric motors, each designed to optimize performance and efficiency for different applications. The most common types include permanent magnets, electromagnets, and switched reluctance magnets.
Permanent magnets, made from materials such as neodymium or ferrite, provide a consistent magnetic field without the need for external power. This type is prevalent in smaller motors where size and weight are critical, such as in robotics and consumer electronics. Their high efficiency and reliability make them a favorite for applications that require a long service life.
On the other hand, electromagnets are used primarily in larger electric motors. These consist of coils of wire that generate a magnetic field when an electric current flows through them. This allows for greater control over the motor’s operation, as the strength and polarity of the magnetic field can be adjusted. Switched reluctance motors utilize a different approach; they rely on the magnetic reluctance (or resistance) to magnetic flux to create motion, offering a simple and robust construction without the need for windings on the rotor. Each type of rotor magnet plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and performance across various electric motor designs.
How Rotor Magnets Interact with Stator Components
The interaction between rotor magnets and stator components is critical for the efficient operation of electric motors. Rotor magnets, typically composed of high-energy materials like neodymium or ferrite, are strategically placed on the rotor to create a magnetic field that interacts with the stator’s winding. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the efficiency of electric motors can be improved by up to 10% through optimized rotor magnet arrangements, demonstrating their significant role in performance enhancement.
As the rotor spins due to an external power source, the magnetic field produced by the rotor magnets induces a corresponding magnetic field in the stator winding. This phenomenon, known as electromagnetic induction, is a fundamental principle of motor operation. The Lorentz force acting on the current-carrying conductors in the stator generates torque, enabling the motor to perform work. Data from the United Nations' Industrial Development Organization reveals that electric motors are responsible for approximately 45% of global electricity consumption in industrial applications, further underscoring the importance of rotor magnet performance in energy efficiency.
The design of rotor magnets also influences the motor's power density and thermal performance. Advanced simulations and material science developments have led to the creation of rotor magnets that withstand higher temperatures while maintaining their magnetic properties. Research published in the IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications indicates that improvements in rotor magnet technology could yield reductions in overall motor size and weight, thus enabling lighter and more efficient machinery that meets the increasing demands of various industrial sectors.
Applications of Rotor Magnets in Various Electric Motor Designs
Rotor magnets play a crucial role in electric motor designs, facilitating efficient energy conversion and improving overall motor performance. In brushless DC motors, for instance, permanent magnets are strategically embedded within the rotor to create a magnetic field that interacts with the stator windings. This interaction generates motion with higher efficiency compared to traditional brushed motors, often achieving efficiency rates above 85%, as reported by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Such motors are widely used in applications ranging from electric vehicles to industrial machinery, where energy efficiency and reliability are paramount.
Additionally, rotor magnets are integral to synchronous motors, which rely on their rotating magnetic field to maintain synchrony with the power supply frequency. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, implementing rotor magnets in these systems can lead to a reduction in energy consumption by up to 30%. Applications in robotics, renewable energy systems, and automation technology illustrate the versatility of rotor magnet configurations. The adoption of rotor magnets not only contributes to enhanced performance but also promotes the trend towards greener technologies by supporting systems that require less energy to operate efficiently.
Applications of Rotor Magnets in Various Electric Motor Designs
Related Posts
-
Why Choose Permanent Magnet Stepper Motors for Your Next Project?
-

Top 7 Benefits of Using Permanent Magnet DC Motors in Modern Applications
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using a Permanent Magnet DC Motor 90V for Your Projects
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Permanent Magnet Motors in Modern Applications
-

Top 5 Benefits of Neodymium Magnet Motors You Need to Know
-

2025 Top 5 Innovations in Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Motor Technology
