Key Differences, Pros, and Cons
When selecting the right motor for precision tasks, two types stand out: stepping motors and servo motors. Both are essential in industries like automation, robotics, and medical devices, but choosing between the two can be challenging.
Understanding their differences, advantages, and limitations can help determine which is best for your specific needs. Let's take a look at the key differences, pros, and cons of stepping motors and servo motors and provide insights on where each performs best.

What are stepping motors?
A stepping motor is a type of DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a series of precise steps. The rotor in a stepping motor moves incrementally with each electrical pulse sent to the stator, allowing for precise position control without the need for additional feedback mechanisms.
How do stepping motors work?
Stepping motors operate by moving the rotor in discrete steps, each typically 1.8 degrees (though finer steps are available). This allows for exact position control.
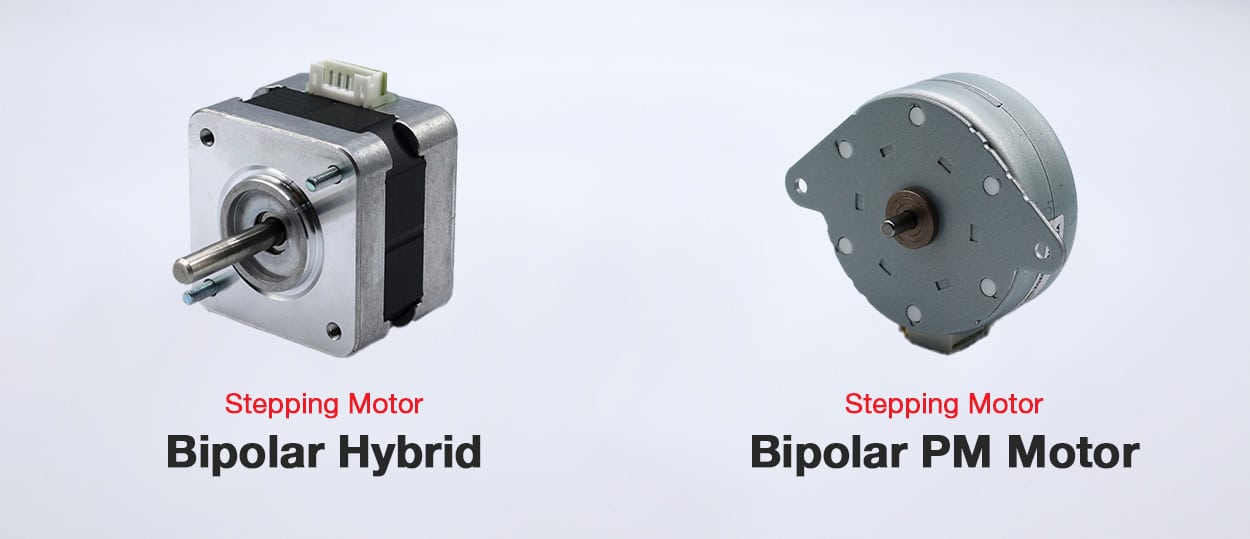
Types of Stepping Motors
Permanent Magnet Stepper (PM): A simple type of stepping motor with a permanent magnet rotor.
Hybrid Stepper Motor: Combines the features of both PM and VR motors, offering superior performance.
Advantages of Stepping Motors
Advantages include high precision and position control, no need for encoders, simple and cost-effective product, they're also ideal for low-moderate speed applications.

What are servo motors?
In contrast to stepping motors, servo motors are rotary actuators that provide precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration using a feedback system. These motors are designed for high-performance applications that require constant monitoring and adjustments to maintain accuracy.
How do servo motors work?
Servo motors use a closed-loop system, where an encoder or potentiometer provides real-time feedback on the rotor's position. This allows the motor to make corrections to maintain precise performance.
Types of servo motor
AC Servo Motors: Powered by AC current, commonly used in high-power applications.
DC Servo Motors: Powered by DC voltage with a built-in feedback mechanism.
Brushless DC (BLDC) Servo Motors: Offer high efficiency, low maintenance, and high performance.
Advantages of servo motors
Some key advantages of servo motors include, their high-efficiency output with consistent torque, smooth operation with precise feedback, their suited to high-speed applications and allow variable speed and load adjustments.
| Features | Stepping Motors | Servo Motors |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Open-loop (no feedback required) | Closed-loop (requires feedback) |
| Precision | High precision, but can lose steps under heavy load | Superior precision with continuous adjustments |
| Torque | High torque at low speeds, drops with increased speed | Consistent torque over a wide range of speeds |
| Speed | Ideal for low to moderate speeds | Performs well at high speeds and variable load |
| Complexity | Simple, easy to implement | Requires complex controllers and feedback systems |
| Cost | Affordable, especially for low-performance applications | Generally more expensive due to complex design and high-performance |
Applications of Stepping Motors and Servo Motors
Stepping Motors
Medical Devices:
In medical applications like insulin pumps and handheld diagnostic tools, miniature stepping motors provide the precise control necessary for dispensing small volumes or positioning components accurately without adding significant bulk.
3D Printers:
Small 3D printers benefit from miniature stepping motors that offer precise control over movement in the X, Y, and Z axes, allowing high-quality, detailed printing even in compact devices.
Consumer Electronics:
Miniature stepping motors are ideal for components that require fine control, such as adjustable lenses in compact cameras or controlled movements in optical devices.
Servo Motors
Medical and Laboratory Equipment:
Miniature servo motors are used in equipment where precise and smooth control is essential, like surgical robots, automated pipetting devices, and lab instruments requiring continuous feedback for positioning.
Automated Smart Home Devices:
Miniature servo motors are ideal for high-precision smart home devices that control lighting, curtain automation, and other adjustable settings, requiring smooth operation and low noise.
Miniaturised Industrial Automation:
Compact industrial machinery and automated inspection systems employ miniature servo motors to achieve precise movements in limited spaces, such as in assembly line applications for small components.


Rotalink’s Gearmotors
Customised Solutions for Precise Applications
At Rotalink, we understand that no two projects are alike. That’s why we are dedicated to providing bespoke gearmotor solutions designed specifically to meet the unique requirements of each application. With our expertise in miniature gearmotors, we collaborate closely with OEMs to deliver products that not only meet performance specifications but also align with space, weight, and operational needs.
Our customisation capabilities allow us to fine-tune everything from torque and speed ratios to gear design, motor configuration, and integration features—ensuring that each solution is optimised for its intended use.