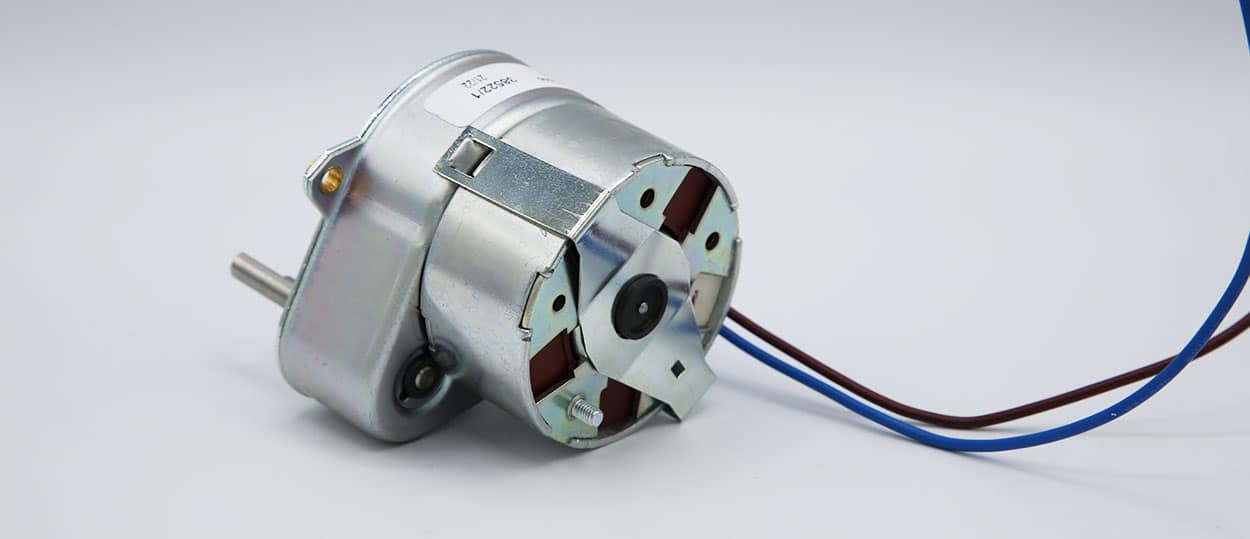
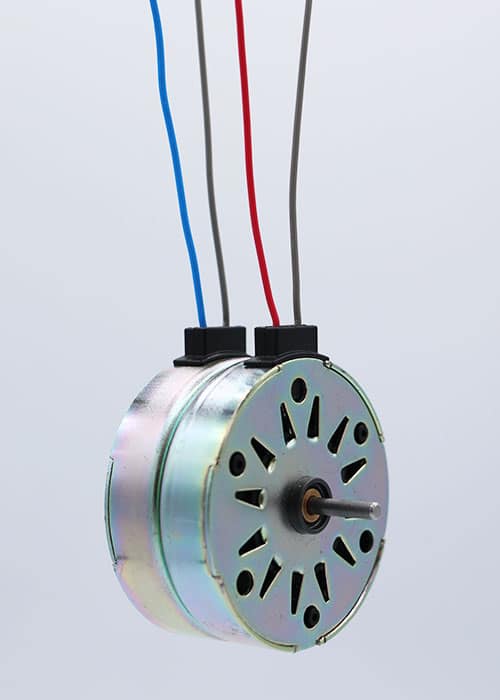
The choice between synchronous and asynchronous motors plays a pivotal role in determining various applications' efficiency, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Both motor types have distinct advantages, and selecting the right one depends on the specific needs of the system in which they will be used. In this article, we’ll explore the key characteristics of each motor, compare their pros and cons, and highlight why asynchronous motors are often the preferred choice for industrial applications.
What is an Asynchronous Motor?
How do asynchronous motors work?
An asynchronous motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. In these motors, the rotor does not rotate at the same speed as the magnetic field produced by the stator; instead, it runs slower, creating a phenomenon called "slip." This difference in speed between the stator’s rotating magnetic field and the rotor’s motion drives the motor.
As the rotor lags behind the stator's field, an electric current is induced, which generates torque. The result is a reliable and durable motor that efficiently converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Key Characteristics of Asynchronous Motors
Slip: The rotor lags behind the rotating magnetic field, which creates the torque needed to power the motor
Induction Principle: No direct electrical connection to the rotor; the rotor's movement is induced by the stator's magnetic field.
AC-Powered: Asynchronous motors typically run on alternating current (AC), making them suitable for various industrial and commercial uses.
Advantages of Asynchronous Motors
Durability: Asynchronous motors are known for their robustness and longevity, making them ideal for demanding environments.
Cost-Effectiveness: Due to their simple design, these motors are relatively inexpensive to manufacture and maintain, offering excellent value for large-scale operations.
Scalability: They can be designed in various sizes, from small applications like fans to large industrial machines.
Common applications of asynchronous motors
Miniature asynchronous motors are used in a wide range of compact devices where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are critical. Their ability to perform well in small spaces makes them an essential component in various industries and applications.
- Home appliances
- Medical equipment
- Industrial automation
- HVAC systems
- Office equipment
What is a Synchronous Motor?
How Do Synchronous Motors Work?
In contrast to asynchronous motors, synchronous motors maintain a constant speed by rotating in exact synchrony with the magnetic field of the stator. This means that the rotor turns at the same speed as the stator’s magnetic field, with no slip involved.
These motors require either a permanent magnet or a separately excited electromagnet on the rotor to create a magnetic field that interacts with the stator. Because of this precise synchronisation, they are commonly used in applications that demand accurate speed and position control.
Key Characteristics of Synchronous Motors
Synchronous Speed: The rotor turns at the same speed as the magnetic field without lagging.
Constant Speed Control: Synchronous motors are known for their precision in speed regulation.
Higher Complexity: These motors generally require additional components, such as slip rings or brushes, for excitation.
Advantages of Synchronous Motors
Precise Speed Control: Ideal for applications where maintaining a constant speed is crucial.
High Efficiency: Particularly at steady loads, synchronous motors can operate very efficiently.
Reliability in High-Precision Tasks: Often used in systems that need exact positioning and speed consistency, like robotics and conveyor belts.
Common applications of synchronous motors
Miniature synchronous motors are widely used in applications that require precision, reliability, and consistent speed control. Their ability to maintain constant speed makes them ideal for tasks where accurate timing or positioning is essential.
- Robotics and automation
- Clocks and timers
- Medical equipment
- Conveyor belts
- Camera systems and optical devices
- turntable motors
Comparing Miniature Asynchronous and Synchronous Motors
Precision vs. Simplicity
While miniature synchronous motors are best suited for tasks that require absolute precision in speed and positioning, miniature asynchronous motors are preferred for their simplicity, durability, and ability to handle fluctuating loads in smaller applications. Asynchronous motors are often the go-to choice for everyday compact devices where high precision isn't required, but cost-effectiveness and reliability are paramount.
Cost and Complexity
Asynchronous motors, with their simpler design, tend to be more affordable, both in terms of manufacturing and maintenance. For small-scale applications where efficiency and durability are more important than exact speed control, they represent a cost-effective solution. Synchronous motors, while offering superior precision, often come at a higher cost due to their additional components and more complex start-up mechanisms.
Rotalink’s Expertise in Asynchronous Motor Solutions
At Rotalink, we specialise in providing high-quality miniature gearmotors for OEMs across a range of industries. Our expertise lies in designing and producing custom motor solutions that meet the specific requirements of our clients, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their products.
We understand that OEM applications often demand compact, efficient motors that can deliver precise torque, speed control, and long-term durability in a small form factor.